DORA: What Financial IT Must Know
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) entered into application across the European Union on 17 January 2025, reshaping how financial institutions manage cyber and operational risk [1]. Although the United...
IP networking is cool! It’s a geeky sentiment, but it’s why I got into IT. But even the geek in me burns out when working network support. I love the skills I’ve gained during routing, wireless, and multicast troubleshooting, but the manual, monotonous tasks that get me. The repetitive tickets, ghost issues, and the false positives can be quite frustrating! Worse, they slow down the resolution of network issues.
NetBrain is a respite from the slow and monotonous manual workflows. When I saw NetBrain Automated Diagnosis in action for the first time, I was floored. Sure, it was amazing, and it changed the entire approach to incident response, but what struck me was how obvious it was. This is how network support should have been for years now. It’s intuitive, but automation technology just couldn’t keep up with our imaginations, until now.
The “proof is in the pudding”, they say, so let’s see a real-world example of typical network issues and how the response looks like under the old, manual workflow vs. the NetBrain automated approach!
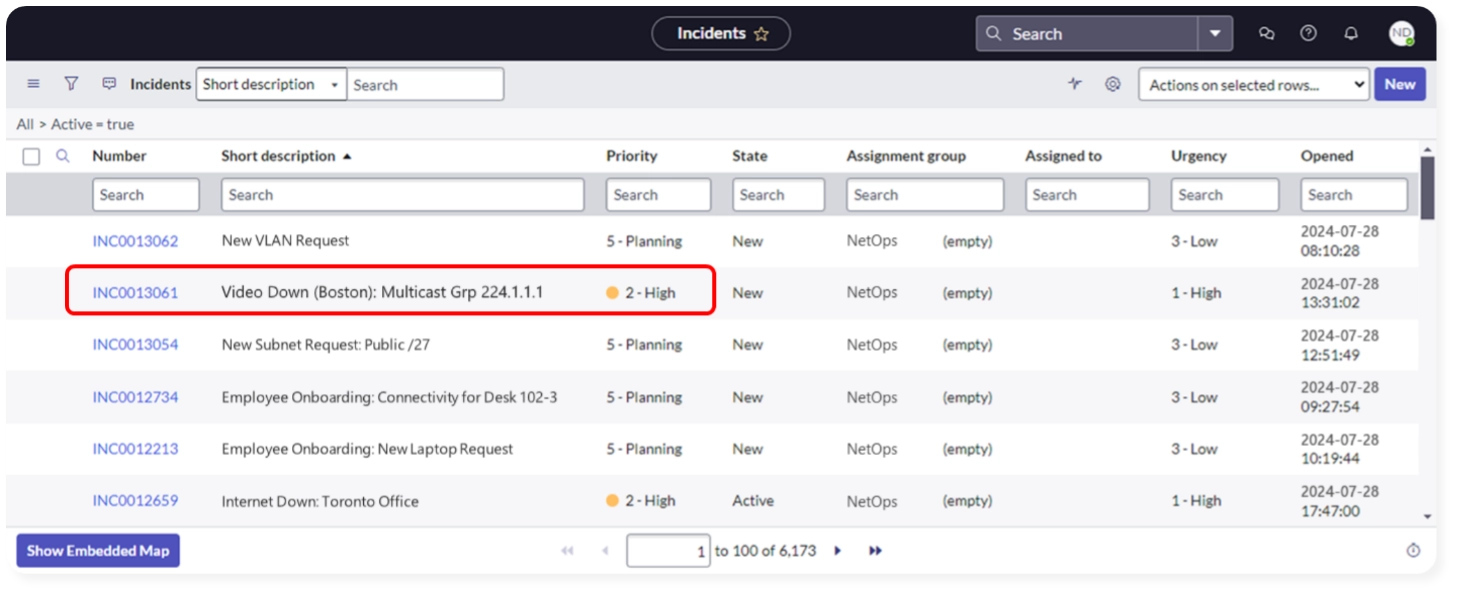
The Scenario: We receive an incident on our ITSM about video multicast down. Looks like multicast troubleshooting is needed.
The Investigation:
Our Boston user VLAN is on router US-BOS-R2. We remote into that router to trace the multicast forwarding upstream. Through a series of CLI commands, we eventually map how the multicast stream should be forwarded and discover an RPF discrepancy caused by a static route. The steps and commands used to identify the root cause are as follows: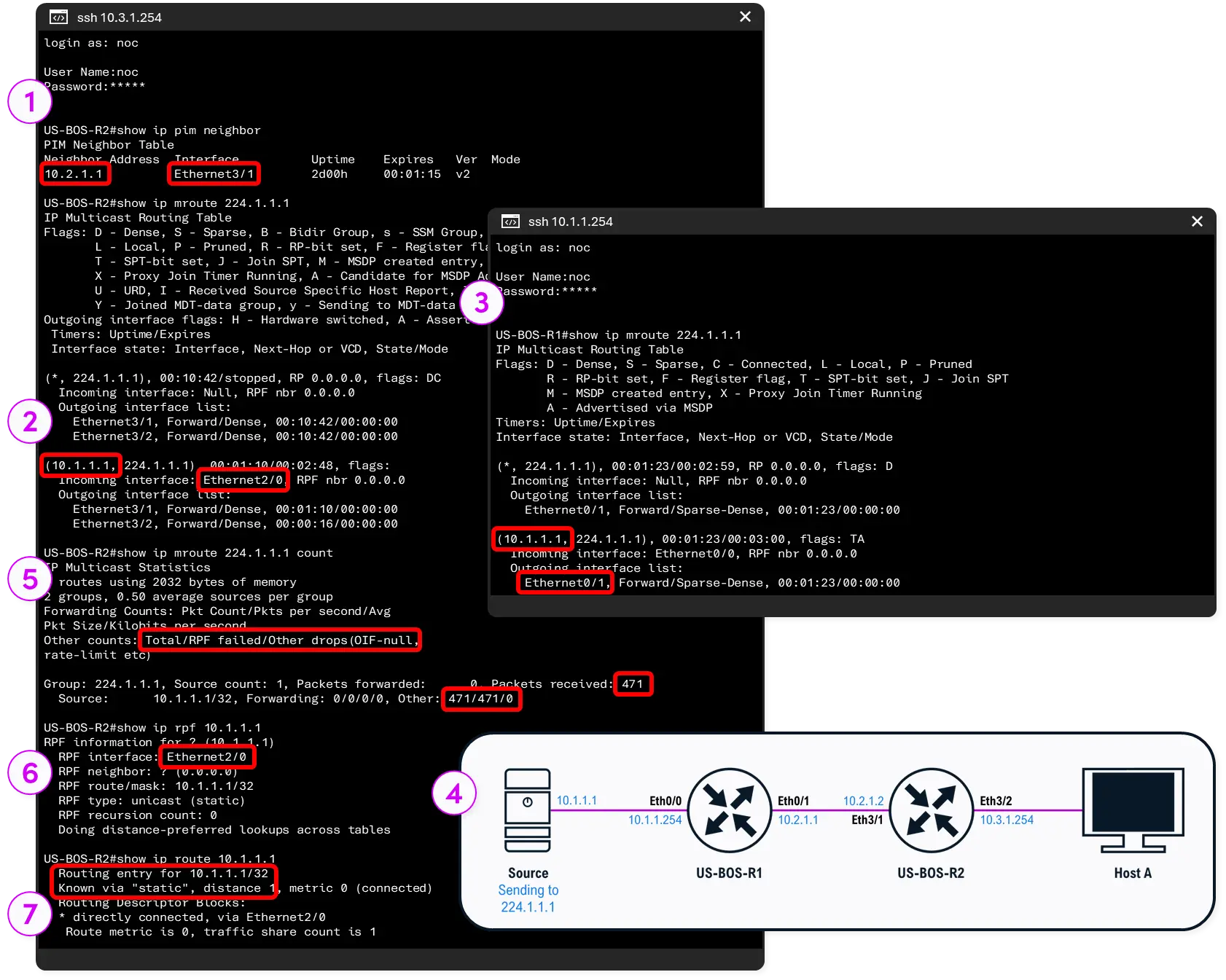
We open the ticket to see the NetBrain automated multicast troubleshooting triggered by our ITSM, click to see the generated map, and see that NetBrain has determined the RPF check has failed due to a static route.

You see how much quicker we can get to actually resolving the multicast troubleshooting issue when we’re not bogged down by the manual information gathering. The time saved isn’t just about how much quicker automation is at pulling data and diagnosing an issue, it’s also about starting the investigation sooner. NetBrain automation goes to work as soon as a ticket is submitted even before a human has a chance to acknowledge it, cutting response times and MTTR dramatically!
Keep an eye out for more “Manual vs. NetBrain Automation” scenarios by subscribing to our blog to understand all the workflows you can evolve with NetBrain automation, including troubleshooting, change management, and outage prevention.